|
| void | Print256Epi32 (__m256i var) |
| |
| void | Print256Epi16 (__m256i var) |
| |
| void | Print256Epi8 (__m256i var) |
| |
| void | Print128Epi8 (__m128i var) |
| |
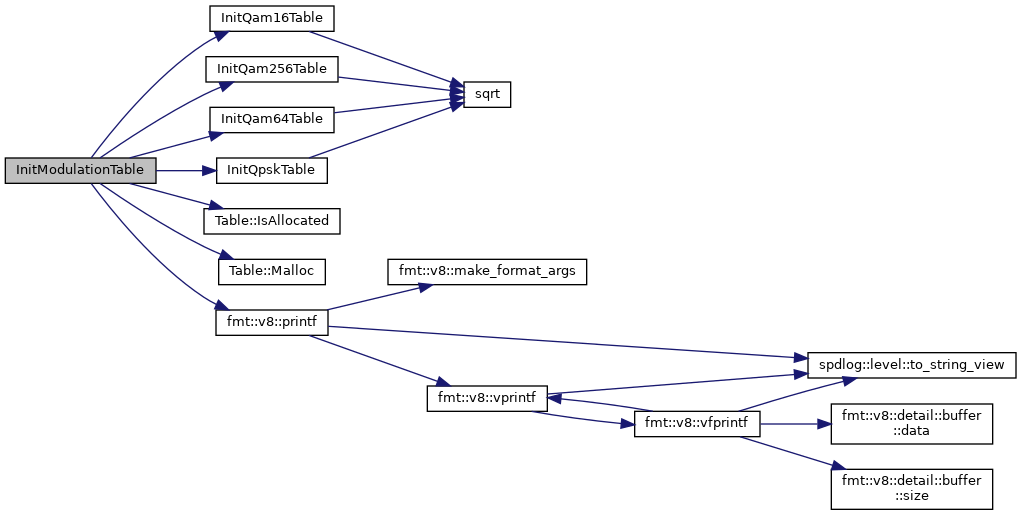
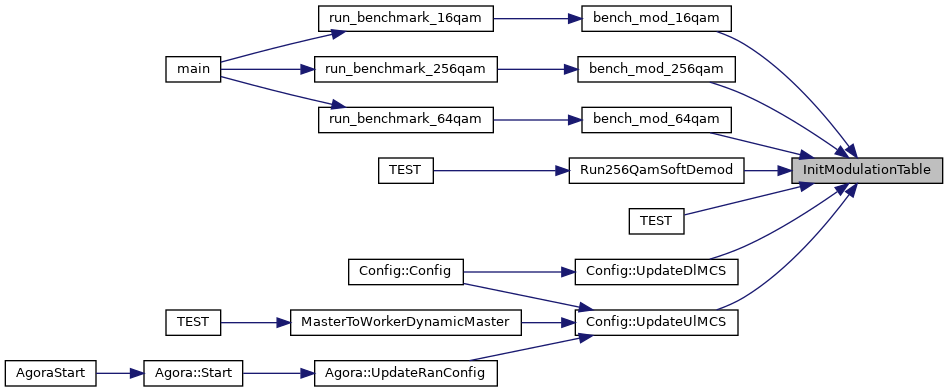
| void | InitModulationTable (Table< complex_float > &mod_table, size_t mod_order) |
| |
| void | InitQpskTable (Table< complex_float > &qpsk_table) |
| |
| void | InitQam16Table (Table< complex_float > &qam16_table) |
| |
| void | InitQam64Table (Table< complex_float > &qam64_table) |
| |
| void | InitQam256Table (Table< complex_float > &qam256_table) |
| |
| complex_float | ModSingle (int x, Table< complex_float > &mod_table) |
| |
| complex_float | ModSingleUint8 (uint8_t x, Table< complex_float > &mod_table) |
| |
| void | ModSimd (uint8_t *in, complex_float *&out, size_t len, Table< complex_float > &mod_table) |
| |
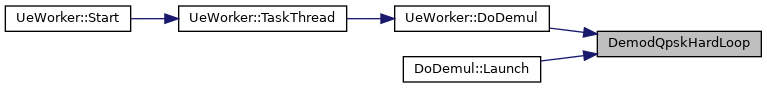
| void | DemodQpskHardLoop (const float *vec_in, uint8_t *vec_out, int num) |
| |
| void | Demod16qamHardLoop (const float *vec_in, uint8_t *vec_out, int num) |
| |
| void | Demod16qamHardSse (float *vec_in, uint8_t *vec_out, int num) |
| |
| void | Demod16qamHardAvx2 (float *vec_in, uint8_t *vec_out, int num) |
| |
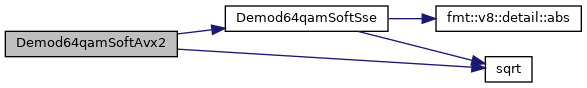
| void | Demod16qamSoftAvx2 (float *vec_in, int8_t *llr, int num) |
| |
| void | Demod64qamHardLoop (const float *vec_in, uint8_t *vec_out, int num) |
| |
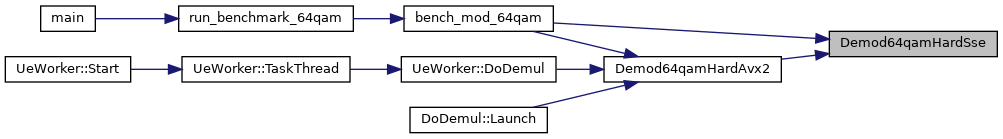
| void | Demod64qamHardSse (float *vec_in, uint8_t *vec_out, int num) |
| |
| void | Demod64qamHardAvx2 (float *vec_in, uint8_t *vec_out, int num) |
| |
| void | Demod64qamSoftAvx2 (float *vec_in, int8_t *llr, int num) |
| |
| void | Demod256qamHardLoop (const float *vec_in, uint8_t *vec_out, int num) |
| |
| void | Demod256qamHardSse (float *vec_in, uint8_t *vec_out, int num) |
| |
| void | Demod256qamHardAvx2 (float *vec_in, uint8_t *vec_out, int num) |
| |
| void | Demod256qamSoftLoop (const float *vec_in, int8_t *llr, int num) |
| |
| void | Demod256qamSoftSse (const float *vec_in, int8_t *llr, int num) |
| |
| void | Demod256qamSoftAvx2 (const float *vec_in, int8_t *llr, int num) |
| |
| void Demod256qamHardLoop |
( |
const float * |
vec_in, |
|
|
uint8_t * |
vec_out, |
|
|
int |
num |
|
) |
| |
256-QAM Modulation Q 01000000 01000010 01001010 01001000 01101000 01101010 01100010 01100000 | 11100000 11100010 11101010 11101000 11001000 11001010 11000010 11000000 01000001 01000011 01001011 01001001 01101001 01101011 01100011 01100001 | 11100001 11100011 11101011 11101001 11001001 11001011 11000011 11000001 01000101 01000111 01001111 01001101 01101101 01101111 01100111 01100101 | 11100101 11100111 11101111 11101101 11001101 11001111 11000111 11000101 01000100 01000110 01001110 01001100 01101100 01101110 01100110 01100100 | 11100100 11100110 11101110 11101100 11001100 11001110 11000110 11000100 01010100 01010110 01011110 01011100 01111100 01111110 01110110 01110100 | 11110100 11110110 11111110 11111100 11011100 11011110 11010110 11010100 01010101 01010111 01011111 01011101 01111101 01111111 01110111 01110101 | 11110101 11110111 11111111 11111101 11011101 11011111 11010111 11010101 01010001 01010011 01011011 01011001 01111001 01111011 01110011 01110001 | 11110001 11110011 11111011 11111001 11011001 11011011 11010011 11010001 01010000 01010010 01011010 01011000 01111000 01111010 01110010 01110000 | 11110000 11110010 11111010 11111000 11011000 11011010 11010010 11010000 ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------— I 00010000 00010010 00011010 00011000 00111000 00111010 00110010 00110000 | 10110000 10110010 10111010 10111000 10011000 10011010 10010010 10010000 00010001 00010011 00011011 00011001 00111001 00111011 00110011 00110001 | 10110001 10110011 10111011 10111001 10011001 10011011 10010011 10010001 00010101 00010111 00011111 00011101 00111101 00111111 00110111 00110101 | 10110101 10110111 10111111 10111101 10011101 10011111 10010111 10010101 00010100 00010110 00011110 00011100 00111100 00111110 00110110 00110100 | 10110100 10110110 10111110 10111100 10011100 10011110 10010110 10010100 00000100 00000110 00001110 00001100 00101100 00101110 00100110 00100100 | 10100100 10100110 10101110 10101100 10001100 10001110 10000110 10000100 00000101 00000111 00001111 00001101 00101101 00101111 00100111 00100101 | 10100101 10100111 10101111 10101101 10001101 10001111 10000111 10000101 00000001 00000011 00001011 00001001 00101001 00101011 00100011 00100001 | 10100001 10100011 10101011 10101001 10001001 10001011 10000011 10000001 00000000 00000010 00001010 00001000 00101000 00101010 00100010 00100000 | 10100000 10100010 10101010 10101000 10001000 10001010 10000010 10000000
bit 7: set if real is positive bit 6: set if imag is positive bit 5: set if real is under threshold 4 bit 4: set if imag is under threshold 4 bit 3: set if real is over threshold 2 and under threshold 6 bit 2: set if imag is over threshold 2 and under threshold 6 bit 1: set between real threshold 5-6 and 2-3 bit 0: set between imag threshold 5-6 and 2-3
| void Demod256qamSoftLoop |
( |
const float * |
vec_in, |
|
|
int8_t * |
llr, |
|
|
int |
num |
|
) |
| |
LLR algorithm derived from paper: Q. Sun and W. Qi, "Soft-demodulation algorithm for 64QAM and it's application in HSPA+," 2012 IEEE 11th International Conference on Signal Processing, 2012, pp. 2309-2312, doi: 10.1109/ICoSP.2012.6492042.
Equations 7, 8, and 9
Same pattern for the final bits. Note that the threshold that is subtracted from is based on the threshold across which the bits revelant to the current LLR flip in the constellation
In addition, the prior LLR that is used essentially gives the distance from a given threshold. For example abs(llr[8 * i + 4]) gives the distance the symbol is from either QAM256_THRESHOLD_2 or QAM256_THRESHOLD_6, whichever is closest.
256-QAM Modulation Q 01000000 01000010 01001010 01001000 01101000 01101010 01100010 01100000 | 11100000 11100010 11101010 11101000 11001000 11001010 11000010 11000000 01000001 01000011 01001011 01001001 01101001 01101011 01100011 01100001 | 11100001 11100011 11101011 11101001 11001001 11001011 11000011 11000001 01000101 01000111 01001111 01001101 01101101 01101111 01100111 01100101 | 11100101 11100111 11101111 11101101 11001101 11001111 11000111 11000101 01000100 01000110 01001110 01001100 01101100 01101110 01100110 01100100 | 11100100 11100110 11101110 11101100 11001100 11001110 11000110 11000100 01010100 01010110 01011110 01011100 01111100 01111110 01110110 01110100 | 11110100 11110110 11111110 11111100 11011100 11011110 11010110 11010100 01010101 01010111 01011111 01011101 01111101 01111111 01110111 01110101 | 11110101 11110111 11111111 11111101 11011101 11011111 11010111 11010101 01010001 01010011 01011011 01011001 01111001 01111011 01110011 01110001 | 11110001 11110011 11111011 11111001 11011001 11011011 11010011 11010001 01010000 01010010 01011010 01011000 01111000 01111010 01110010 01110000 | 11110000 11110010 11111010 11111000 11011000 11011010 11010010 11010000 ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------— I 00010000 00010010 00011010 00011000 00111000 00111010 00110010 00110000 | 10110000 10110010 10111010 10111000 10011000 10011010 10010010 10010000 00010001 00010011 00011011 00011001 00111001 00111011 00110011 00110001 | 10110001 10110011 10111011 10111001 10011001 10011011 10010011 10010001 00010101 00010111 00011111 00011101 00111101 00111111 00110111 00110101 | 10110101 10110111 10111111 10111101 10011101 10011111 10010111 10010101 00010100 00010110 00011110 00011100 00111100 00111110 00110110 00110100 | 10110100 10110110 10111110 10111100 10011100 10011110 10010110 10010100 00000100 00000110 00001110 00001100 00101100 00101110 00100110 00100100 | 10100100 10100110 10101110 10101100 10001100 10001110 10000110 10000100 00000101 00000111 00001111 00001101 00101101 00101111 00100111 00100101 | 10100101 10100111 10101111 10101101 10001101 10001111 10000111 10000101 00000001 00000011 00001011 00001001 00101001 00101011 00100011 00100001 | 10100001 10100011 10101011 10101001 10001001 10001011 10000011 10000001 00000000 00000010 00001010 00001000 00101000 00101010 00100010 00100000 | 10100000 10100010 10101010 10101000 10001000 10001010 10000010 10000000
To generate this table, first create a 4 bit gray code. Then, generate a vector of the scales you want for your QAM table. Finally, use the gray code values for each index (0-15) to select the scale value you assign to that index in this array. This means that if you take the index of each scale in this table, and order those indicies by the value of the scale the index refers to, you will have a gray code